Introduction
African music is one of the oldest and most diverse musical traditions in the world, deeply rooted in culture, storytelling, and identity. Beyond its entertainment value, African music has served as a historical record, a tool for resistance, and a bridge to the global music scene. While many recognize Africa’s influence on global genres, the deeper history of African music and its unsung heroes remain lesser known. In this blog post, we uncover the hidden stories, key figures, and pivotal moments that have shaped the African musical landscape.
The Ancient Origins of African Music
Music has been a fundamental part of African societies for millennia, with drums, flutes, and string instruments dating back thousands of years.
The Oldest African Instruments
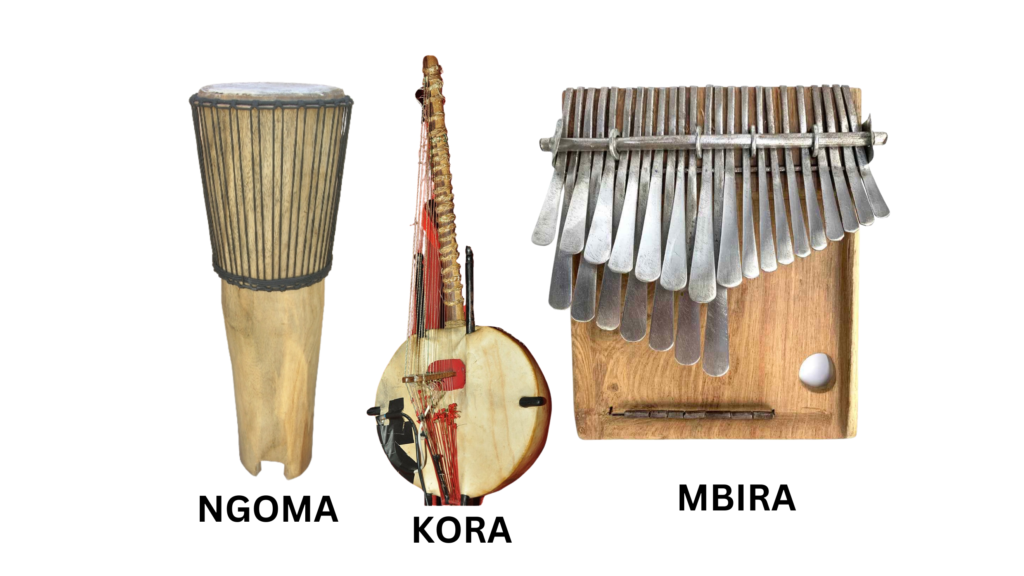
The ngoma drums of Central Africa were used in communication, spiritual ceremonies, and war preparations.
The kora, a 21-string harp-lute, has been played by griots (oral historians) in Mali and Senegal for over 700 years.
The mbira (thumb piano) of the Shona people in Zimbabwe, dating back at least 1,000 years, was used to connect with ancestors.
Music as a Storytelling Tradition
Example: The Griot tradition in West Africa, where skilled musicians and poets preserve genealogies, social customs, and history through music. Long before written records, African societies passed down history and wisdom through song.
African Music as a Tool of Resistance and Revolution
Throughout history, African music has played a crucial role in resisting oppression and uniting communities against injustice.
Freedom Songs in the Anti-Colonial Struggle
In South Africa, songs like “Senzenina?” (What Have We Done?) became anthems of resistance during apartheid. Miriam Makeba’s “Soweto Blues” captured the pain of the 1976 Soweto Uprising, making her a global voice for justice.
Fela Kuti and the Afrobeat Revolution
Nigerian musician Fela Kuti used his Afrobeat sound to criticize government corruption and injustice. His song “Zombie” mocked military dictatorship, making him a target of the Nigerian government.
The Role of Reggae in Africa’s Liberation Movements
Bob Marley’s “Zimbabwe” became an anthem of independence for the country, with Marley invited to perform at Zimbabwe’s liberation ceremony in 1980.
Lucky Dube of South Africa used reggae to spread anti-apartheid messages and call for African unity.
Unsung Heroes of African Music
While many African musicians have gained international fame, some pioneers have had a profound influence but remain lesser known.
E.T. Mensah – The Father of Highlife (Ghana)
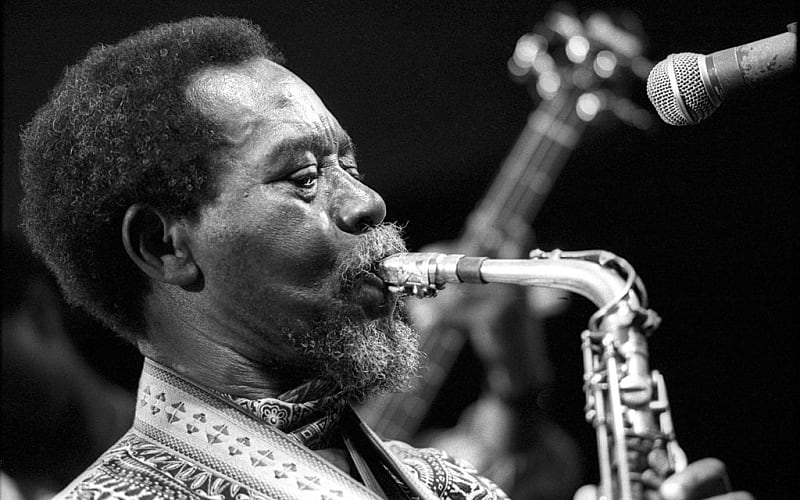

Blended indigenous African rhythms with jazz and swing, pioneering the highlife genre in the 1940s. Inspired later genres like Afrobeats and hiplife.
Brenda Fassie – South Africa’s Queen of Pop
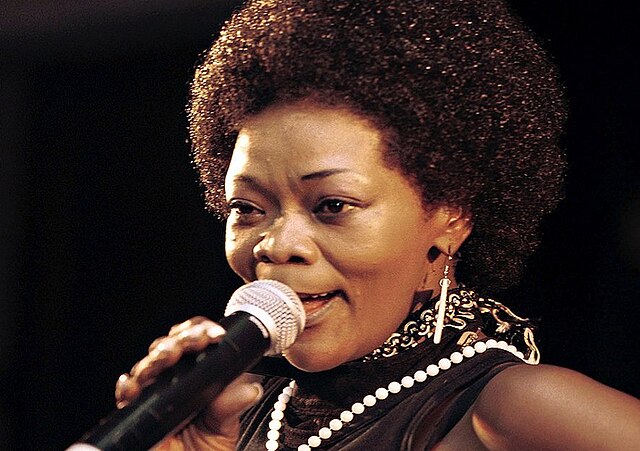

Her hit “Black President” honored Nelson Mandela and became a symbol of anti-apartheid activism. She brought African pop music to a new level with her socially conscious lyrics and fearless personality.
Ali Farka Touré – The Desert Blues Guitar Legend (Mali)
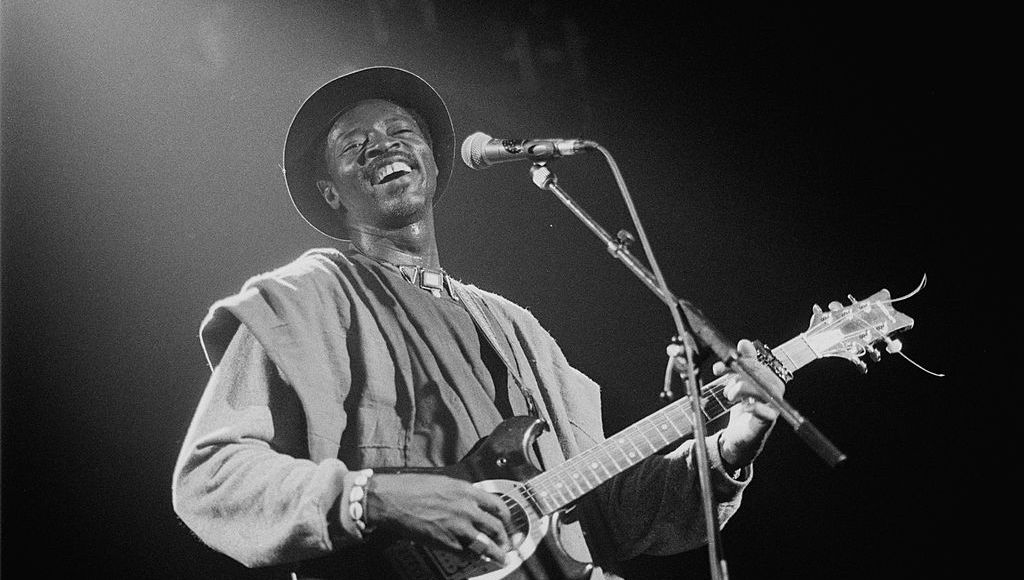

Fused traditional Malian rhythms with the blues, influencing American musicians like John Lee Hooker. His work proved that the blues originated in Africa, tracing back to Malian musical traditions.
Key Moments in African Music History
The Birth of Afrobeats and Afropop
A fusion of highlife, jazz, and funk that has evolved into today’s global Afrobeats movement, led by artists like Burna Boy and Wizkid.
The Rise of Amapiano
A deep house and jazz-influenced genre that originated in South Africa in the 2010s and became a global sensation via TikTok.
The First African Grammy Award Winners
Miriam Makeba (1966) became the first African artist to win a Grammy. In recent years, artists like Burna Boy, Angelique Kidjo, and Tems have continued the legacy.
African Music’s Influence on Global Sounds
Africa’s rhythms, melodies, and instruments have shaped many global genres, from jazz to hip-hop.
| Genre | African Influence |
| Jazz | African drumming patterns influenced early jazz rhythms. |
| Hip-Hop | Call-and-response techniques from African chants are common in rap music. |
| Latin Music | African percussion forms the base of salsa, merengue, and samba. |
| Blues | Originated from West African griot traditions. |
The Contribution of African Music to Humanity and Civilization
African music has not only influenced global music genres but has also contributed to shaping human civilization in profound ways:
Cultural Preservation and Identity
Music serves as an archive of African history, preserving languages, traditions, and oral storytelling across generations. The griot tradition in West Africa ensured that communities retained their history even before the advent of written records.
Rhythmic Foundations of World Music
African rhythm structures have provided the basis for countless global music styles, from Latin salsa to rock and roll. Example: African polyrhythms directly influenced jazz and blues, which later evolved into rock and hip-hop.
Social Movements and Change
African music has historically played a crucial role in liberation movements, providing a voice for the oppressed and inspiring revolutions. Example: Songs from the anti-apartheid movement in South Africa spread messages of unity and defiance worldwide.
Healing and Spirituality
Traditional African drumming and chanting have been used for spiritual healing, meditation, and mental wellness. Many African cultures believe that music holds the power to connect with ancestors and invoke spiritual blessings.
Education and Knowledge Transfer
Folk songs and traditional chants have been used as teaching tools, passing down lessons in morality, discipline, and communal values. Example: Work songs used by African slaves in the Americas became the foundation of gospel and blues, shaping modern Western music.
Challenges in Documenting and Preserving African Music History
| Challenge | Solution |
| Loss of Traditional Music Due to Westernization | Support local music education and preservation efforts. |
| Limited Documentation of African Musical Pioneers | Establish digital archives and oral history projects. |
| Copyright and Ownership Issues | Strengthen laws to protect African artists from exploitation. |
| Lack of Representation in Global Music Spaces | Promote African-led music festivals and record labels. |
Conclusion
The history of African music is vast, rich, and deeply intertwined with the struggles, triumphs, and evolution of the continent. From ancient griots to modern Afrobeats superstars, African music continues to shape global culture. Its rhythms, messages, and traditions have not only influenced entertainment but also played a major role in civilization, social change, and human connection. By preserving its history and celebrating its heroes, we ensure that the heartbeat of Africa remains strong and continues to inspire future generations.

Leave a Reply